What is DNA replication, and why is it essential for life?
DNA replication is the process by which DNA makes a copy of itself. This process is essential for cell division, growth, and repair. Without DNA replication, cells would not be able to divide, and life would not be possible.
DNA replication is a complex process that involves many different proteins and enzymes. The process begins when the DNA double helix unwinds and the two strands separate. Each strand then serves as a template for the synthesis of a new strand of DNA. The new strands are complementary to the original strands, meaning that they have the same sequence of nucleotides. Once the new strands are synthesized, they are joined together to form a new double helix.
DNA replication is a highly accurate process, but errors can occur. These errors can lead to mutations, which are changes in the DNA sequence. Mutations can be harmful, beneficial, or neutral. Beneficial mutations can give an organism a competitive advantage, while harmful mutations can lead to disease.
DNA replication is essential for life. Without DNA replication, cells would not be able to divide, and life would not be possible.
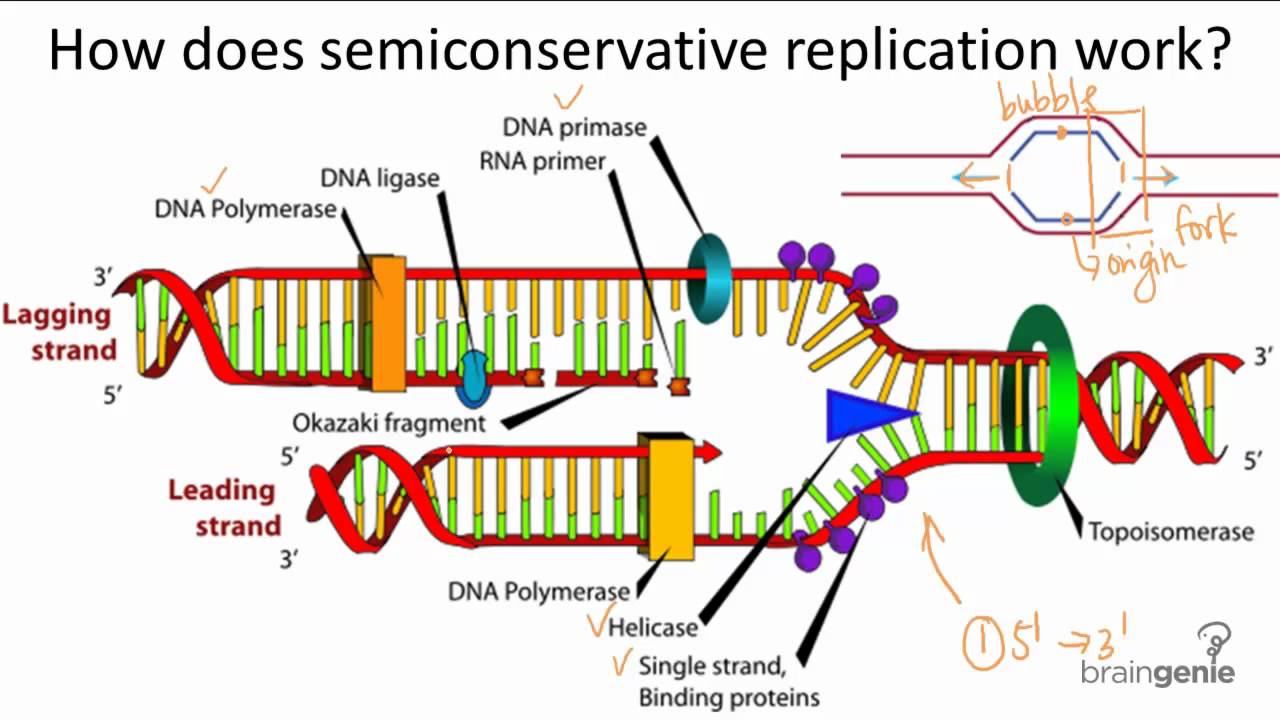
DNA Replication Semiconservative
DNA replication is the process by which DNA makes a copy of itself. This process is essential for cell division, growth, and repair. DNA replication is semiconservative, which means that each new DNA molecule consists of one original strand and one newly synthesized strand.
- Template-dependent: DNA replication requires a template strand to guide the synthesis of the new strand.
- Semiconservative: Each new DNA molecule consists of one original strand and one newly synthesized strand.
- Accurate: DNA replication is a highly accurate process, but errors can occur.
- Essential for life: DNA replication is essential for cell division, growth, and repair.
- Mechanism: DNA replication occurs in three main steps: initiation, elongation, and termination.
- Errors: Errors in DNA replication can lead to mutations, which can be harmful, beneficial, or neutral.
- Regulation: DNA replication is regulated by a variety of proteins and enzymes.
DNA replication is a complex and essential process. It is essential for the growth and survival of all living organisms.
Template-dependent
DNA replication is a template-dependent process, meaning that it requires a template strand to guide the synthesis of the new strand. This template strand is one of the two original strands of the DNA double helix. The new strand is synthesized by DNA polymerase, which adds nucleotides to the growing strand in a complementary fashion. This means that the sequence of nucleotides in the new strand is complementary to the sequence of nucleotides in the template strand.
- Accuracy: The template-dependent nature of DNA replication ensures that the new strand is an accurate copy of the original strand. This is essential for the faithful transmission of genetic information from one generation to the next.
- Semiconservative replication: The template-dependent nature of DNA replication also ensures that DNA replication is semiconservative. This means that each new DNA molecule consists of one original strand and one newly synthesized strand.
- Errors: Despite the high accuracy of DNA replication, errors can occur. These errors can lead to mutations, which are changes in the DNA sequence. Mutations can be harmful, beneficial, or neutral.
The template-dependent nature of DNA replication is essential for the accurate transmission of genetic information. It ensures that each new DNA molecule is an accurate copy of the original DNA molecule.
Semiconservative
The semiconservative nature of DNA replication is a fundamental principle of molecular biology. It states that each new DNA molecule consists of one original strand and one newly synthesized strand. This is in contrast to the conservative model of DNA replication, which proposed that each new DNA molecule consists of two original strands.
- Evidence for semiconservative replication: The semiconservative nature of DNA replication was first demonstrated by the Meselson-Stahl experiment in 1958. In this experiment, Escherichia coli were grown in a medium containing heavy nitrogen (15N). The DNA of these bacteria was then extracted and centrifuged in a density gradient. The results showed that the DNA formed two bands, one containing heavy DNA and one containing light DNA. This indicated that the DNA had replicated semiconservatively, with each new DNA molecule consisting of one heavy strand and one light strand.
- Mechanism of semiconservative replication: DNA replication occurs by a process called semiconservative replication. In this process, the two strands of the DNA double helix separate, and each strand serves as a template for the synthesis of a new strand. The new strands are synthesized by DNA polymerase, which adds nucleotides to the growing strand in a complementary fashion. This means that the sequence of nucleotides in the new strand is complementary to the sequence of nucleotides in the template strand.
- Importance of semiconservative replication: The semiconservative nature of DNA replication is essential for the accurate transmission of genetic information. It ensures that each new DNA molecule is an accurate copy of the original DNA molecule.
The semiconservative nature of DNA replication is a fundamental principle of molecular biology. It is essential for the accurate transmission of genetic information.
Accurate
DNA replication is a highly accurate process, but errors can occur. These errors can lead to mutations, which are changes in the DNA sequence. Mutations can be harmful, beneficial, or neutral. Beneficial mutations can give an organism a competitive advantage, while harmful mutations can lead to disease.
The accuracy of DNA replication is essential for the survival of all living organisms. If DNA replication were not accurate, then mutations would accumulate and eventually lead to the death of the organism. The semiconservative nature of DNA replication helps to ensure its accuracy. This is because each new DNA molecule consists of one original strand and one newly synthesized strand. This means that any errors that occur during DNA replication are only present in the newly synthesized strand. The original strand can then be used as a template to correct the errors in the newly synthesized strand.
The accuracy of DNA replication is also important for the transmission of genetic information from one generation to the next. If DNA replication were not accurate, then the DNA sequences of offspring would not be identical to the DNA sequences of their parents. This could lead to a loss of genetic information and eventually to the extinction of species.
The semiconservative nature of DNA replication is a fundamental principle of molecular biology. It is essential for the accurate transmission of genetic information and for the survival of all living organisms.
Essential for life
DNA replication is essential for life because it is the process by which cells make copies of their DNA. This process is essential for cell division, growth, and repair.
Cell division is the process by which cells divide into two new cells. DNA replication is essential for cell division because it ensures that each new cell has a complete copy of the DNA. Without DNA replication, cell division would not be possible, and cells would not be able to grow or repair themselves.
DNA replication is semiconservative, which means that each new DNA molecule consists of one original strand and one newly synthesized strand. This is important because it ensures that each new cell has a complete copy of the original DNA molecule.
The semiconservative nature of DNA replication is essential for the accurate transmission of genetic information from one generation to the next. It ensures that each new organism has a complete copy of the DNA from its parents.
DNA replication is a complex and essential process. It is essential for the growth and survival of all living organisms.
Mechanism
DNA replication is a complex process that occurs in three main steps: initiation, elongation, and termination. These steps are tightly regulated to ensure that DNA replication is accurate and complete.
- Initiation: Initiation is the first step of DNA replication. It begins when a protein complex called the replisome binds to the DNA at a specific location called the origin of replication. The replisome then unwinds the DNA double helix and separates the two strands.
- Elongation: Elongation is the second step of DNA replication. It occurs when DNA polymerase adds nucleotides to the 3' end of each new strand. DNA polymerase can only add nucleotides that are complementary to the nucleotides on the template strand. This ensures that the new strand is an accurate copy of the original strand.
- Termination: Termination is the final step of DNA replication. It occurs when the replisome reaches the end of the DNA molecule. The replisome then releases the new DNA molecule and the two new DNA molecules are annealed together to form a double helix.
The three steps of DNA replication are essential for the accurate and complete replication of DNA. These steps are tightly regulated to ensure that DNA replication is faithful and that errors are minimized.
Errors
During DNA replication, errors can occur that lead to changes in the DNA sequence. These changes are called mutations. Mutations can be harmful, beneficial, or neutral. Beneficial mutations can give an organism a competitive advantage, while harmful mutations can lead to disease. Neutral mutations have no effect on the organism.
The semiconservative nature of DNA replication plays an important role in the Entstehung of mutations. Because each new DNA molecule consists of one original strand and one newly synthesized strand, any errors that occur during DNA replication are only present in the newly synthesized strand. The original strand can then be used as a template to correct the errors in the newly synthesized strand.
The semiconservative nature of DNA replication helps to ensure that mutations are rare. However, mutations do occur, and they can have a significant impact on the organism. Mutations can lead to new traits, which can be beneficial or harmful. Mutations can also lead to diseases, such as cancer.
The study of mutations is important for understanding how organisms evolve. Mutations are the raw material for evolution. Without mutations, evolution would not be possible.
Regulation
DNA replication is a complex and essential process that is regulated by a variety of proteins and enzymes. These proteins and enzymes ensure that DNA replication is accurate and complete.
The semiconservative nature of DNA replication is essential for its accurate regulation. This is because each new DNA molecule consists of one original strand and one newly synthesized strand. This means that any errors that occur during DNA replication are only present in the newly synthesized strand. The original strand can then be used as a template to correct the errors in the newly synthesized strand.
The proteins and enzymes that regulate DNA replication are essential for the accurate transmission of genetic information. These proteins and enzymes ensure that each new cell has a complete and accurate copy of the DNA.
The regulation of DNA replication is a complex and essential process. It is essential for the growth and survival of all living organisms.
FAQs about DNA Replication Semiconservative
DNA replication is the process by which DNA makes a copy of itself. This process is essential for cell division, growth, and repair. DNA replication is semiconservative, which means that each new DNA molecule consists of one original strand and one newly synthesized strand.
Question 1: What is the difference between conservative and semiconservative DNA replication?
Conservative DNA replication is a hypothetical model of DNA replication in which each new DNA molecule consists of two original strands. Semiconservative DNA replication is the actual model of DNA replication in which each new DNA molecule consists of one original strand and one newly synthesized strand.
Question 2: What is the role of DNA polymerase in DNA replication?
DNA polymerase is an enzyme that adds nucleotides to the 3' end of each new strand during DNA replication. DNA polymerase can only add nucleotides that are complementary to the nucleotides on the template strand. This ensures that the new strand is an accurate copy of the original strand.
Question 3: What is the importance of the semiconservative nature of DNA replication?
The semiconservative nature of DNA replication is important because it ensures that each new cell has a complete and accurate copy of the DNA. This is essential for the accurate transmission of genetic information from one generation to the next.
Question 4: What are the potential consequences of errors in DNA replication?
Errors in DNA replication can lead to mutations, which are changes in the DNA sequence. Mutations can be harmful, beneficial, or neutral. Beneficial mutations can give an organism a competitive advantage, while harmful mutations can lead to disease.
Question 5: How is DNA replication regulated?
DNA replication is regulated by a variety of proteins and enzymes. These proteins and enzymes ensure that DNA replication is accurate and complete.
Question 6: What is the significance of DNA replication in living organisms?
DNA replication is essential for the growth and survival of all living organisms. It is the process by which cells make copies of their DNA, which is necessary for cell division, growth, and repair.
Summary: DNA replication is a complex and essential process that is essential for the accurate transmission of genetic information. It is regulated by a variety of proteins and enzymes to ensure that it is accurate and complete.
Transition to the next article section: DNA replication is a fundamental process in molecular biology. It is essential for understanding how cells grow and divide, and how genetic information is passed from one generation to the next.
Conclusion
DNA replication is a fundamental process in molecular biology. It is essential for understanding how cells grow and divide, and how genetic information is passed from one generation to the next. DNA replication is semiconservative, which means that each new DNA molecule consists of one original strand and one newly synthesized strand. This ensures that each new cell has a complete and accurate copy of the DNA.
The semiconservative nature of DNA replication is essential for the accurate transmission of genetic information. It ensures that each new cell has a complete and accurate copy of the DNA. This is essential for the growth and survival of all living organisms.
Julia Gisella's Battle With Cancer: Tragic Loss And Enduring Legacy
Unveiling The Power Of Glance.Inuit: A Comprehensive Guide
Bernie Bernice Baker Miracle Young | Trailblazing American Politician

Question Video Understanding the Products of Semiconservative DNA
10.2.2 Semiconservative Replication YouTube
Dna Replication Semiconservative Biological Science Picture Directory